Jason B Gibbons et al. Sci Rep. 2022.
Abstract
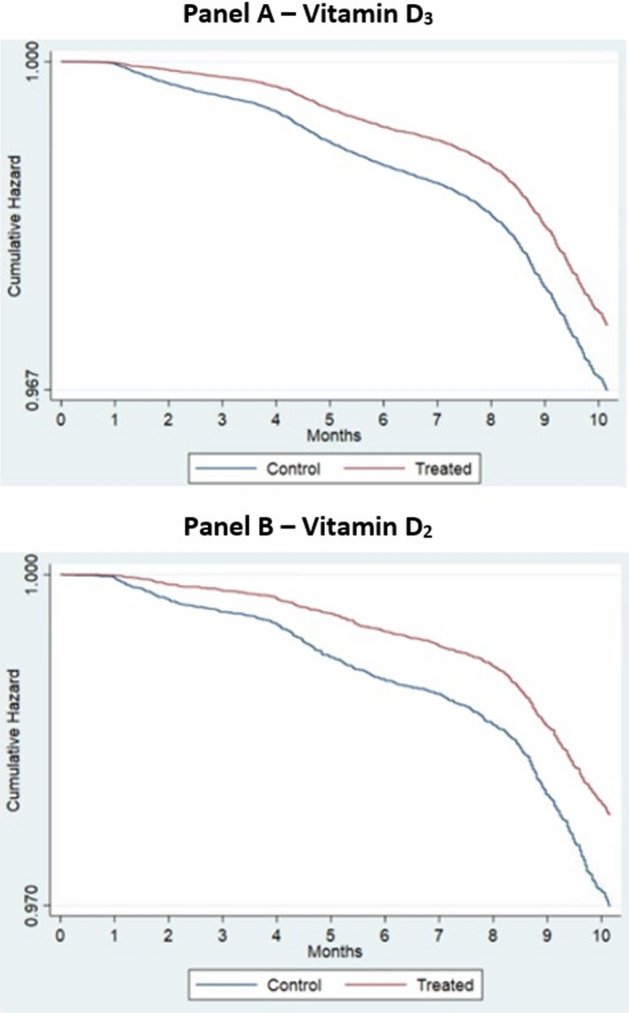
Vitamin D deficiency has long been associated with reduced immune function that can lead to viral infection. Several studies have shown that Vitamin D deficiency is associated with increases the risk of infection with COVID-19. However, it is unknown if treatment with Vitamin D can reduce the associated risk of COVID-19 infection, which is the focus of this study. In the population of US veterans, we show that Vitamin D2 and D3 fills were associated with reductions in COVID-19 infection of 28% and 20%, respectively [(D3 Hazard Ratio (HR) = 0.80, [95% CI 0.77, 0.83]), D2 HR = 0.72, [95% CI 0.65, 0.79]]. Mortality within 30-days of COVID-19 infection was similarly 33% lower with Vitamin D3 and 25% lower with D2 (D3 HR = 0.67, [95% CI 0.59, 0.75]; D2 HR = 0.75, [95% CI 0.55, 1.04]). We also find that after controlling for vitamin D blood levels, veterans receiving higher dosages of Vitamin D obtained greater benefits from supplementation than veterans receiving lower dosages. Veterans with Vitamin D blood levels between 0 and 19 ng/ml exhibited the largest decrease in COVID-19 infection following supplementation. Black veterans received greater associated COVID-19 risk reductions with supplementation than White veterans. As a safe, widely available, and affordable treatment, Vitamin D may help to reduce the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Discover more from Rich Kilchrist RDN LDN Registered Dietitian & Licensed Nutritionist
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
